100 Percent Renewable Cities - Is Your Mayor Smarter Than a 5th Grader?
Mayors in more than 100 U.S. cities have announced plans to transition their electrical power systems to 100 percent renewable by 2050. They propose replacement of traditional coal, natural gas, and nuclear-generating stations with wind, solar and wood-fired stations. But none of these mayors have a plausible idea of how to meet their commitment.
In December, Cincinnati became the 100th U.S. city to commit to 100 percent electricity from renewable sources, with a target to achieve this goal by 2035. Cincinnati Mayor John Cranley said, “It has become clear that cities will lead the global effort to fight climate change, and Cincinnati is on the front lines.” Cleveland Mayor Frank Jackson also pledged to reach 100 percent renewable electricity by 2050 as part of the city’s 2018 Climate Action Plan.
But these announcements appear to be a folk tale worthy of the Brothers Grimm. In 2018, renewables provided less than 3 percent of Ohio’s electricity, which came 47 percent from coal, 35 percent from natural gas and 15 percent from nuclear generators. Mayors Cranley and Jackson appear to have failed to consider the cost or scale of their energy change commitments.
As part of the effort, the Ohio Power Siting Board recommended the approval of the Icebreaker Wind Facility last July. The Icebreaker project would initially construct six 3.5-megawatt wind turbines in Lake Erie, ten miles off the coast of Cleveland, at an estimated cost of $126 million. The project would annually produce only about 75 gigawatt-hours of electricity, but plans call for an expansion to over 1,000 offshore wind towers.
Renewable energy is fashionable, but also expensive. The Icebreaker wind turbines cost $21 million each, or about six times the U.S. market price for wind turbines, which is about $1 million per megawatt. The cost of expansion to 1,000 turbines would approach $20 billion. These renewable system costs will be in addition to existing power generation plants, 90 percent of which must be maintained to provide security of electricity supply when the wind doesn’t blow and the sun doesn’t shine.
In 2017, Ohio residents consumed 119,000 gigawatt-hours of electrical power. If completed, the 1,000 wind turbines of the expanded $20 billion Icebreaker project would deliver about 12,000 gigawatt-hours, or only about 10 percent of Ohio’s electricity need.
Minneapolis Mayor Jacob Frey and St. Paul Mayor Melvin Carter pledged their cities to 100 percent renewables by 2030. Major wind system build-outs during the last five years boosted Minnesota to the 8th-leading wind energy state in the United States. Renewables now provide about 27 percent of the state’s electricity. But Minnesota residents are paying for it. Over the last nine years, Minnesota power prices increased 34 percent, compared to the US average price rise of 7 percent.
In Wisconsin, Madison Mayor Paul Soglin announced last July the city’s commitment to 100 percent renewable electricity by 2050. But Wisconsin is not exactly the sun belt. Traditional generating stations provide 92 percent of the state’s electrical power and Wisconsin is a poor location for both wind and solar.
Not to be deterred, the City of Madison announced in 2017, a contract for five “utility-scale” solar arrays that would deliver 20 megawatt-hours of electricity per year. But Wisconsin consumes 65,000 gigawatt-hours of electricity each year. More than three million such “utility-scale” solar projects would be needed to supply just one percent of Wisconsin’s electricity.
City officials in Atlanta pledged to reach 100 percent renewables by 2035, but have been honest about the fact that they don’t know how to do it. Only about 6 percent of Atlanta’s electricity comes from renewable sources, about the same amount as the state of Georgia. So, Atlanta proposes purchasing large amounts of renewable energy credits from wind and solar generators in other states, so that they can claim their green energy status.
Energy does not have color. No one can tell whether the electricity from their wall outlet is green or provided by a coal-fired plant. Purchasing renewable credits from other locations is the sleight-of-hand method that allows city mayors to claim 100 percent renewable status.
Maybe these mayors have learned a way to spin climate change straw into gold. Cincinnati, Cleveland, Minneapolis, St. Paul, Atlanta and several other cities will receive $2.5 million grants from the Bloomberg Philanthropies group of billionaire Michael Bloomberg for their efforts to “fight climate change.” Unfortunately, these grants will only be a drop in the bucket compared to the billions in additional electricity costs that citizens will pay for renewable electricity programs.
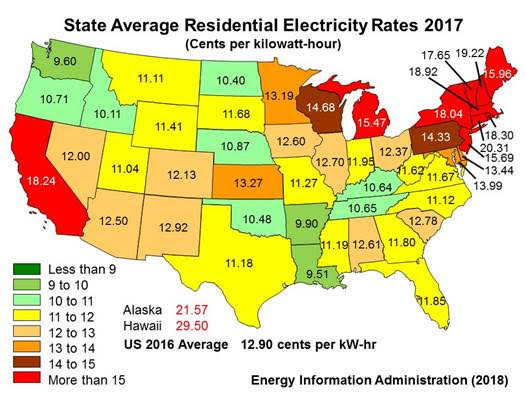
California is the center of the 100-percent-renewables fable. More than 30 California cities have committed to 100 percent renewable electricity, including San Diego, San Francisco and San Jose, as well as the state of California itself. The state is doing a great job of boosting electricity prices. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, California 2017 residential electricity prices were 18.2 cents per kilowatt-hour, about 50 percent higher than any other state in the West. Look for California rates to double in the next two decades, driven by efforts to achieve high penetration of renewables.
So is your mayor smarter than a fifth grader? When it comes to energy policy, maybe not.
Steve Goreham is a speaker on the environment, business and public policy. He’s also the author of the book, “Outside the Green Box: Rethinking Sustainable Development.”
CORRECTION, Feb. 25, 2019: We have made two corrections to this Op-Ed at the request of the Public Utilities Commission of Ohio, which contacted the writer directly about them.
First, we have corrected “As part of the effort, the Ohio Power Siting Board approved the Icebreaker Wind Facility last July” to “As part of the effort, the Ohio Power Siting Board recommended the approval of the Icebreaker Wind Facility last July.”
Second, in the same paragraph, we corrected “six 3.5-gigawatt wind turbines” to “six 3.5-megawatt wind turbines.”
Though The Western Journal did not originate these errors, we did publish them, and are therefore responsible for them. We apologize for any confusion the misinformation may have caused.
The views expressed in this opinion article are those of their author and are not necessarily either shared or endorsed by the owners of this website. If you are interested in contributing an Op-Ed to The Western Journal, you can learn about our submission guidelines and process here.
Truth and Accuracy
We are committed to truth and accuracy in all of our journalism. Read our editorial standards.
Advertise with The Western Journal and reach millions of highly engaged readers, while supporting our work. Advertise Today.











